K2 – cheap and on the rise
Interesting 8 minute report from the streets of New York. Follow a Vice News reporter as she tags along with NY medics dealing with K2/spice users.
From VICE NEWS…
Interesting 8 minute report from the streets of New York. Follow a Vice News reporter as she tags along with NY medics dealing with K2/spice users.
From VICE NEWS…
1-12-2015
Business owners who maintain drug free workplaces and/or supervisors of employees who are subject to reasonable suspicion drug testing need to be educated about their role in the drug free workplace, and understand how to properly intervene in situations where they believe an employee may be abusing drugs. Unfortunately many companies “wing it” when dealing with employees who they suspect may be under the influence of prohibited substances. This often leads to ineffective handling of the situation, and may leave the company vulnerable to a lawsuit if improperly handled. What is reasonable suspicion training for supervisors?
At a minimum, an effective training program would include:
Untrained supervisors can be a liability to your organization.
Any business owner, employee or supervisor who has the ability to initiate a reasonable suspicion drug or alcohol test in the workplace.
It’s a federal requirement (FMCSA, FAA, PHMSA, FTA, USCG as well as DOE) to ensure that any employee with the authority to initiate a reasonable cause test complete 60/60 min. drug/alcohol training awareness and reasonable suspicion signs and symptoms training. Failure to complete training is a violation of federal law. See dot regulations. However, any company with a drug testing policy that allows for reasonable suspicion drug testing should have their supervisors trained. Training will result in a more effective drug testing program and may reduce your exposure to lawsuits.
Recently drug use is on the rise. (see WSJ) and employees who abuse substances may go to great lengths to hide their use. Millions of full-time worker’s are abusing drugs today. Substance abusers are less productive, use more healthcare, and can be a danger to your employees and the general public.
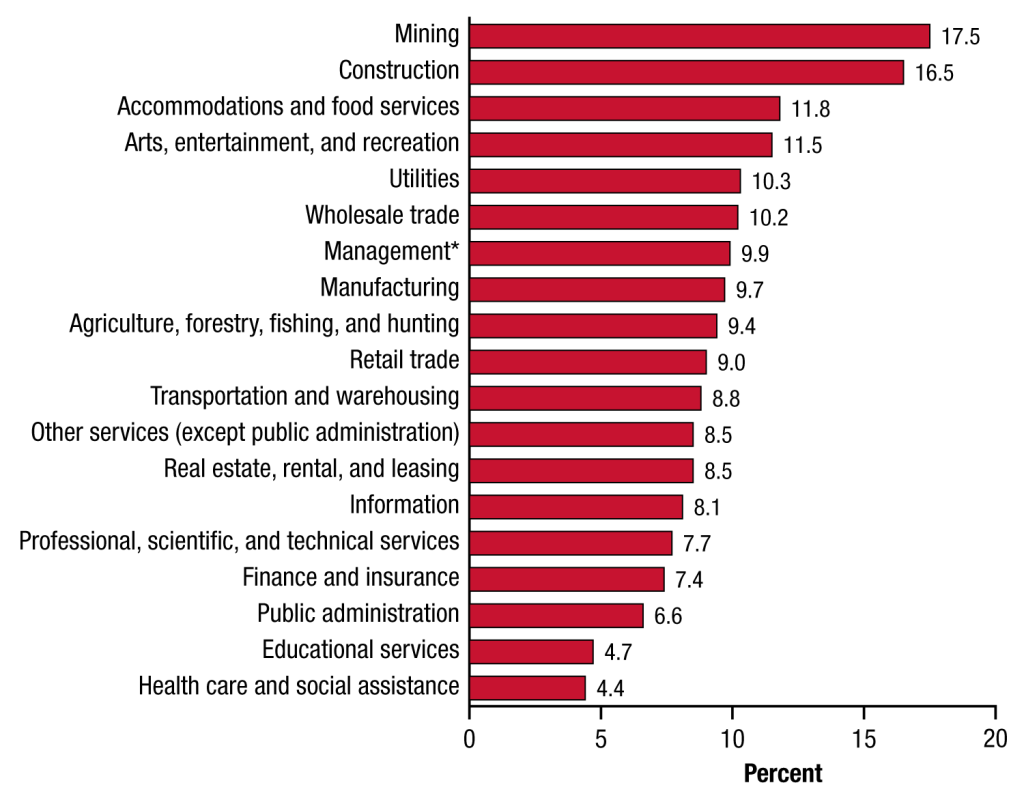
Past month heavy alcohol use among adults aged 18 to 64 employed full time, by industry category: combined 2008 to 2012 – SAMSHA.
There are a variety of methods you can perform training. In-person via a drug testing consultant, via DVD, or online (AtHandTraining offers DOT and drug free workplace versions here). Each has their own benefit however, we here at AtHandTraining provide only online training for the following reasons:
Unless your regulated by the FAA (who requires 12-18 month recurring training), DOT supervisors only need to take 60 minutes or drug and 60 minute of alcohol (total 2 hours) once during their employ. DOT best practices recommend retraining every two years. We recommend retraining for all drug free workplace supervisors every two years.
Regardless of what method you choose just be sure to utilize formal training of some sort to help maintain an effective drug testing program providing a safer workplace for your employees.
While you’re at it, you might consider ensuring your employees fully understand prohibited behaviors by enrolling them in a drug and alcohol awareness course.
AtHandTraining.com provides awesome online training for reasonable suspicion training for supervisors and employees subject to drug and alcohol testing.
Buy now and begin training in minutes!
$37 or Less – Buy DOT Supervisor Course
$11 or less – Buy DOT Employee Drug Awareness Course
The Governor’s Highway Safety Administration (GHSA) recently released a “state’s guide” to drugged driving report prepared by Dr. James Hedlund. The report gleams data from the last 20 years and seeks to provide states with action items they can take to address the risiing issue of drugged driving. The GHSA assembled an panel of experts that included state officials, researchers and national organizations that guided the project.
AtHandTraining took a look at the report to draw out some of the more relevant information that workplace safety managers might find interesting. You can check out the entire 51 page report here however here are some highlights below:
(1) (Compton and Berning, 2015; Hartman and Huestis, 2013; Kelly-Baker, 2014).
(2) (Hartman and Huestis, 2013)
AtHandTraining.com provides awesome online training for DOT Supervisor reasonable suspicion training and for DOT employees for drug and alcohol awareness training.
Buy now and begin training in minutes!